
How Quick Commerce Data Scraping Can Be a Game-Changer in Stock Inventory Optimization
Published on October 3, 2025
The rise of quick commerce (Q-commerce) platforms like Zepto, Blinkit, Swiggy Instamart, and Dunzo has redefined customer expectations in the e-commerce and grocery delivery industry. With deliveries promised in 10 to 30 minutes, inventory management has shifted from weekly restocking to real-time stock replenishment.
To remain competitive and operationally efficient in this lightning-fast retail environment, businesses must constantly monitor trends, stock levels, product demand, and availability—not only within their own systems but across competitors’ platforms as well.
This is where quick commerce data scraping becomes a game-changer. By programmatically extracting real-time data from Q-commerce apps and websites, companies can make smarter inventory decisions, optimize fulfillment, and avoid stockouts or overstocking.
In this blog, we’ll explore how scraping data from Q-commerce platforms fuels inventory optimization and business growth.
1. What Is Quick Commerce Data Scraping?
Q-commerce data scraping is the process of extracting structured information from online quick commerce platforms using web crawling or APIs. This includes data points like:
- Product availability
- Real-time stock indicators
- Pricing and discounts
- Delivery slots or ETAs
- Store-specific listings
- Location-specific product catalogs
This scraped data can be used to monitor competitors, study regional demand, optimize pricing, and—most importantly—refine your stock and inventory decisions.
2. Why Inventory Optimization Matters in Q-Commerce
In traditional retail, inventory is replenished based on weekly or monthly demand forecasts. In Q-commerce, the window is minutes or hours. Failing to adapt inventory strategies results in:
- Missed sales due to stockouts
- Wasted inventory due to overstocking perishable goods
- Poor customer satisfaction from unavailable high-demand items
- Increased logistics costs due to frequent, unscheduled restocking
Quick commerce scraping lets businesses anticipate demand and stock patterns by analyzing competitor availability and trends in real time.
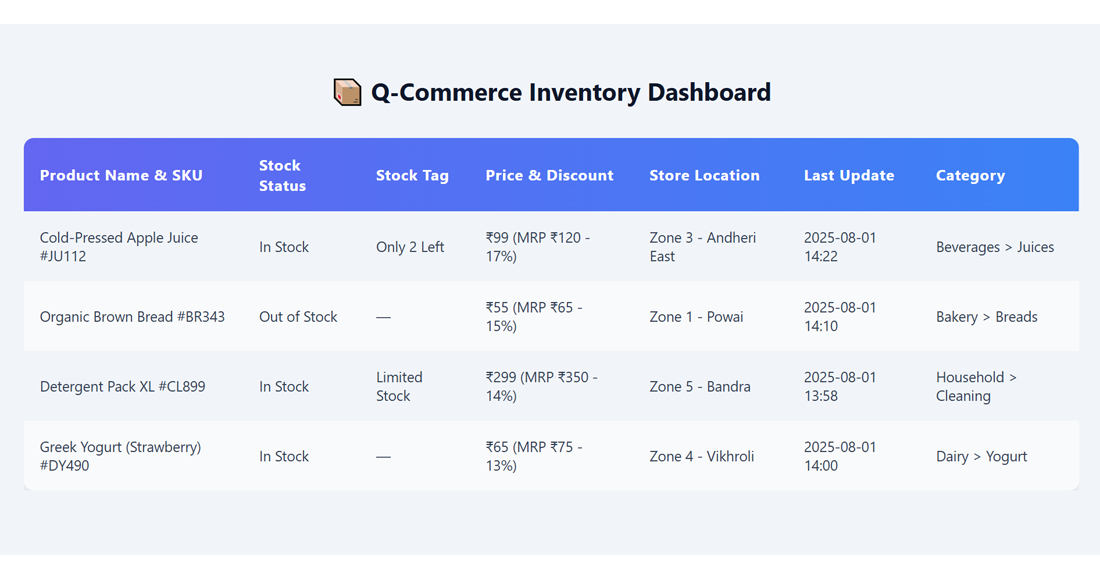
3. What Kind of Data Can Be Scraped from Q-Commerce Apps?
Here’s a breakdown of key inventory-related data points that can be scraped:
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Product Name & SKU | Identifying the specific product in stock |
| In-Stock / Out-of-Stock | Availability status of a product in real-time |
| Quantity or Stock Tags | "Only 2 left", "Limited stock", etc. |
| Price & Discount | Base price, MRP, discount percentage |
| Store / Location Name | Dark store or zone from which the item is shipped |
| Time of Update | Timestamp to track the frequency of availability |
| Category & Subcategory | E.g., Beverages > Juices > Cold-Pressed |
4. How Scraping Q-Commerce Data Optimizes Inventory
1. Real-Time Stock Visibility of Competitors
By scraping stock availability from Blinkit, Zepto, or Instamart by PIN code, you can:
- Detect which products are running out in certain zones
- Restock fast-moving SKUs before demand spikes
- Identify gaps in competitor listings
Example: If Zepto marks "Cold Brew Coffee" as out of stock in Mumbai zones, you can ensure you're stocked up and run targeted ads to grab market share.
2. Dynamic Demand Forecasting
Use availability signals, search trends, and discounts to:
- Predict what’s selling fast by region and time of day
- Prepare warehousing for peak hours (e.g., 6–9 PM)
- Estimate reorder frequency with historical scrape data
This makes your forecasting models hyper-local and timely.
3. Reduce Stockouts and Overstock Risks
Scraped data reveals:
- What time of day or week do products run out
- How long do competitors stay stocked after discounts
- Average inventory holding per product per store
This data informs your buffer stock strategy to avoid over-ordering or missing sales.
4. Identify Inventory Blind Spots
Scraping helps you identify:
- Products you don’t stock but competitors do
- Products you stock but competitors don’t (blue ocean)
- Underperforming SKUs that have excess inventory
This allows you to optimize your catalog and eliminate dead stock.
5. Location-Based Stock Planning
Since Q-commerce platforms serve specific pin codes or local zones, data scraping can help you:
- Stock up SKUs that are high in demand in Zone A but low in Zone B
- Use hyperlocal demand data to drive warehouse stocking
- Localize offers and promotions based on zone-level availability
5. Sample Workflow: Scraping Stock Data from Zepto or Blinkit
Here’s a simplified approach to scraping product inventory from Blinkit’s web interface:
Tools Required:
- Python
- requests, BeautifulSoup
- Proxy and User-Agent rotation
- pandas for CSV output
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import pandas as pd
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0'
}
url = 'https://blinkit.com/cn/breakfast-cereals'
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
soup = BeautifulSoup(response.text, 'html.parser')
products = soup.find_all('div', class_='productCard')
data = []
for item in products:
name = item.find('div', class_='product-title').text.strip()
price = item.find('span', class_='price').text.strip()
stock = 'In Stock'
if 'out-of-stock' in str(item):
stock = 'Out of Stock'
data.append([name, price, stock])
df = pd.DataFrame(data, columns=['Product', 'Price', 'Availability'])
df.to_csv('blinkit_stock_data.csv', index=False)For advanced setups, use headless browsers like Selenium or Playwright to scrape JavaScript-heavy platforms like Instamart or Zepto.
6. Real-World Use Cases
| Business Type | Benefit from Q-Commerce Scraping |
|---|---|
| FMCG Brands | Track product visibility and availability on all platforms |
| Retailers & Distributors | Know which zones need urgent replenishment |
| Dark Store Operators | Hyper-local demand forecasting |
| Q-Commerce Startups | Benchmark inventory coverage against competitors |
| CPG Analysts | Study real-time performance by location |
7. Tools & Technologies for Scalable Q-Commerce Scraping
| Tool / Stack | Use Case |
|---|---|
| Scrapy | Large-scale scraping |
| Selenium/Playwright | Handle JavaScript-rendered apps |
| BeautifulSoup | Lightweight HTML parsing |
| Proxy Manager | Avoid getting blocked |
| Airflow or CRON | Schedule regular scraping |
| PostgreSQL / MongoDB | Store structured inventory records |
8. Best Practices for Ethical Scraping
- Scrape only public data (not behind login)
- Rotate IPs and User-Agents to avoid blocking
- Respect robots.txt (or throttle responsibly)
- Use scraped data internally, not for resale
- Avoid frequent polling that may hurt site performance
9. Challenges & Solutions
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Location-based pricing or stock | Use PIN code-based session scraping |
| JavaScript-rendered inventory tags | Use Selenium or Playwright |
| Frequent structure changes | Use dynamic XPath or ML parsing models |
| Bot detection & CAPTCHA | Rotate proxies and use headless browsers |
10. Conclusion
In a retail world that moves at the speed of Q-commerce, static inventory planning is no longer effective. Businesses that embrace real-time, scraped inventory intelligence from Blinkit, Zepto, and Instamart will gain a clear advantage in:
- Forecasting regional demand
- Reducing waste and stockouts
- Improving operational efficiency
- Capturing market share through smarter stocking
Scraping Q-commerce data isn't just a tech trick—it's a strategic enabler for supply chain agility and business growth.

